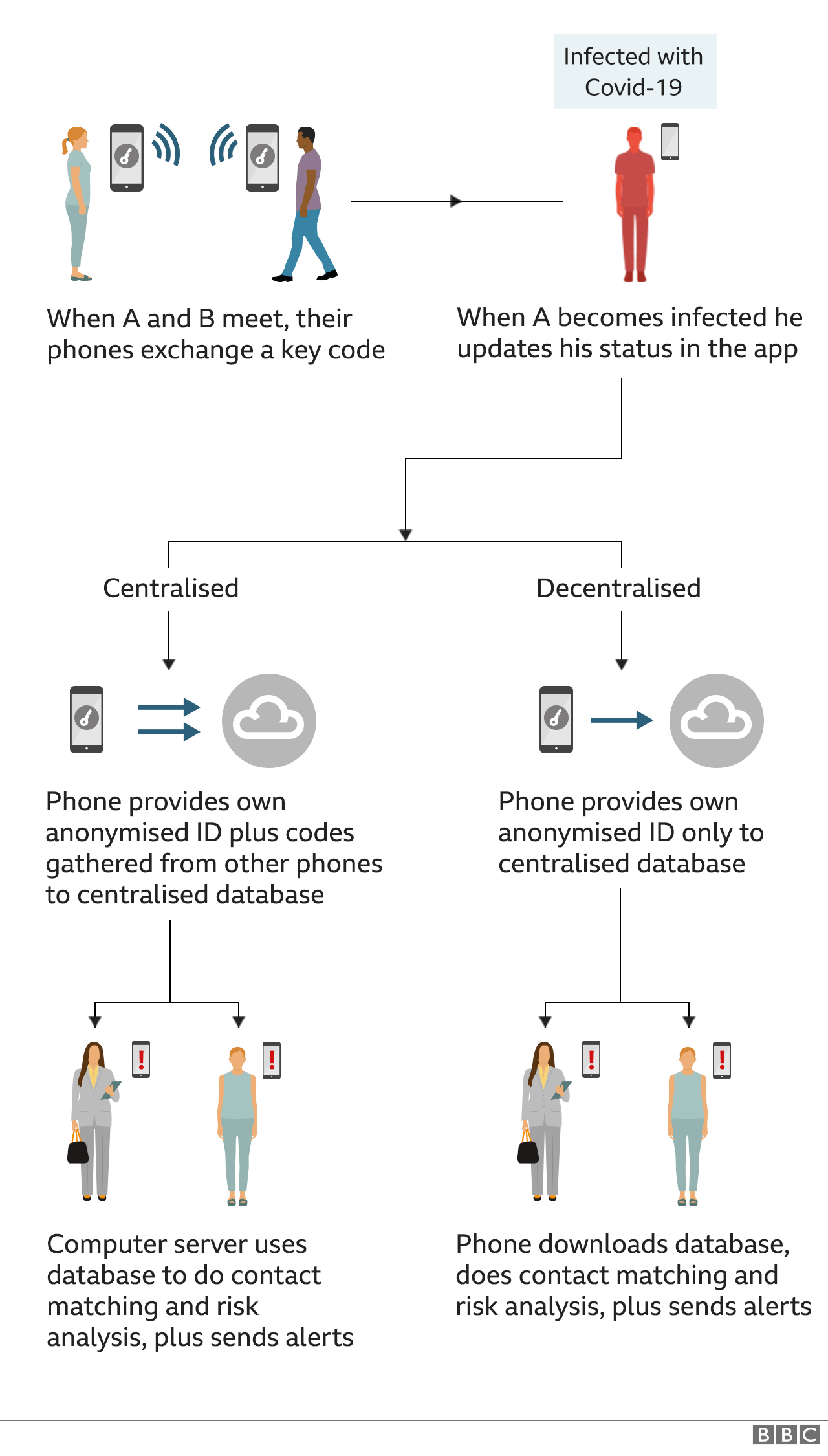
The Apple-Google model carries the process out on the handsets themselves, making it more difficult for the authorities or potential hackers to de-anonymize the records and use them for other means.
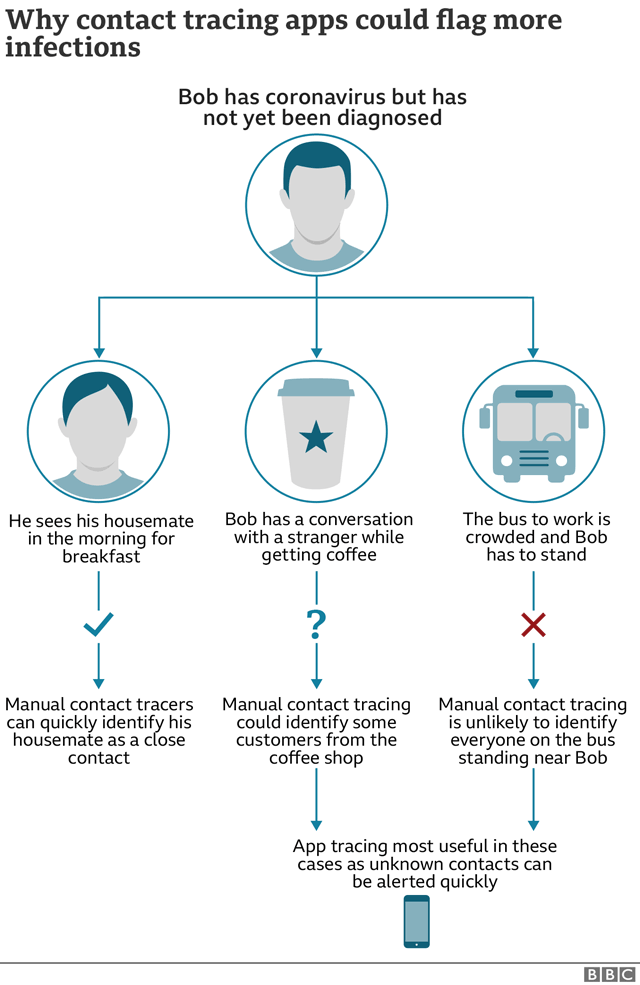
Digital contact tracing replaces at least some of those interviews with technology. Especially in South Korea and China, it's been an effective way to keep infections down. (South Korea is finally down to zero local infections.) But the successful approaches used elsewhere rely on a level of trust in authority and giving up privacy, which may not be acceptable in the individualistic United States.
Your mobile phone carrier can track your location at all times, by analyzing cell tower connections. This depends on the cell signal strength. In South Korea, when someone is diagnosed with COVID-19, those tower hits are being shared with local governments, which combine them with CCTV footage, credit card receipts, and interviews, and broadcast the results on the web and through text messaging.
Bluetooth-based contact-tracing apps such as Singapore's TraceTogether rely on phones running the app in the background, searching for nearby Bluetooth devices also running the app—that's how Apple's AirDrop works. Phones can roughly determine the distance between each other based on Bluetooth signal strength; recent iPhones can also use their U1 ultra-wideband chips to figure out their proximity to each other. Unlike the network and QR-code-based solutions, Bluetooth-based apps drain your phone's battery.